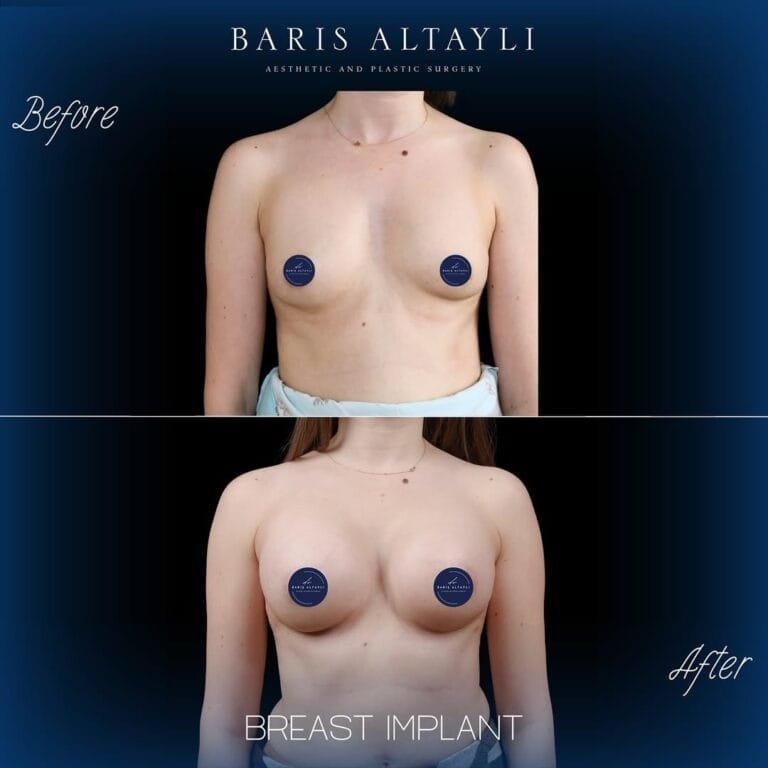
Breast augmentation is one of the most popular cosmetic surgeries worldwide. But a common concern is:
Can a woman’s body reject breast implants?
The short answer: It’s very rare — but possible.
Breast implants are made from materials that are designed to be biocompatible, meaning they’re generally accepted by the body. However, in some cases, the body may respond negatively to the implant, leading to what some refer to as “rejection.” While not common, it’s important to understand the signs and what to do if complications arise.
What Does “Rejection” Really Mean?
The term “rejection” isn’t typically used in the medical community for breast implants the same way it is for organ transplants. Instead, adverse reactions or complications may occur, including:
- Capsular contracture (the most common issue)
- Infection
- Implant rupture or leakage
- Inflammatory response
- Implant extrusion (extremely rare)
These conditions can cause discomfort, visible changes, or require implant removal.
Signs Your Body Might Be Reacting to Implants
If your body is having a reaction, symptoms may include:
- Persistent pain or discomfort
- Hardening or distortion of the breast
- Redness or warmth at the surgical site
- Fever or flu-like symptoms
- Swelling that doesn’t go down
- Changes in breast shape or position
Any of these signs should be evaluated by a qualified plastic surgeon immediately.
Risk Factors That Can Increase Complications
✔ Smoking or poor wound healing
✔ Autoimmune disorders
✔ Previous infections or implant issues
✔ Incorrect implant placement or size
✔ Not following post-op instructions
How Common Are Serious Reactions?
| Complication | Frequency | Treatable? |
|---|---|---|
| Capsular contracture | ~5–10% of cases | Yes |
| Infection | <2% | Yes |
| Rupture (saline/silicone) | 1–3% per 10 years | Yes (requires replacement) |
| Implant rejection | Extremely rare (less than 1%) | Usually |
How to Lower Your Risk
To minimize the chance of your body reacting to implants:
- Choose a board-certified plastic surgeon
- Follow all aftercare instructions
- Avoid smoking and alcohol during recovery
- Choose appropriate implant size and placement
- Attend follow-up appointments regularly
Frequently Asked Questions
Can implants be removed if there’s a reaction?
Yes. In some cases, implants may need to be removed or replaced if complications are serious or persistent.
Does the body treat silicone implants differently from saline?
Both types are considered safe. Silicone may feel more natural, but the body’s reaction is similar for both.
What is capsular contracture?
It’s when scar tissue tightens around the implant, causing the breast to feel firm or painful. It’s the most common implant complication.
Can breast implants cause autoimmune symptoms?
Some women report symptoms like fatigue or joint pain, sometimes called breast implant illness (BII). Research is ongoing, and a direct link hasn’t been medically confirmed.
Should I worry about rejection before getting implants?
It’s very rare. As long as you’re in good health and choose an experienced surgeon, your risk is extremely low.
Conclusion
Yes, a woman’s body can have a negative reaction to breast implants, but true rejection is extremely rare. Most complications are treatable and preventable with good surgical care and proper aftercare. The key is to stay informed, monitor your healing, and communicate with your surgeon at every step.